The Hawai‘i State Kagawaran ng Edukasyon’s budget plays a crucial role in supporting student success and maintaining the quality of our public school system. Our budget is divided into two main parts: the operating budget and the Capital Improvements Program (CIP) budget.
Appropriation → | → Allocation → | → Allotment → | → Expenditure |
Resources that have been or are in the process of being approved by the Legislature and have become law. (Legislative Reference Bureau – The Badyet Process) | Appropriation amounts provided (“allocated”) to programs to create expenditures plans. Allocated amount could be less than Appropriation due to restrictions set forth by the Governor or by the Department depending on the fiscal conditions of the time. | Once the Expenditure plans are completed and approved, resources are loaded (“allotted”) into the Financial Management System allowing programs to begin spending their allotted resources. | Actual use of the resources for payroll and by either purchasing or encumbering goods or services. |
The $2.18 billion operating budget for fiscal year 2024-25, primarily funded by state tax revenue, covers the day-to-day operations of schools and mga opisina, from teacher salaries to classroom resources. Meanwhile, the CIP budget focuses on the development, maintenance and upgrading of school facilities, funded almost entirely through state bonds.
Together, these budgets ensure that our schools are equipped to provide a safe, engaging and effective learning environment for all students. Learn more about the Department’s budgets below.
TIMELINE
This is a timeline of major events of the Department’s operating budget appropriations.
Petsa | Organisasyon | Description |
|---|---|---|
1/16/2026 | Hawaiʻi State Legislature | Senate Committees on Ways and Means and Education Budget Briefing for the Kagawaran ng Edukasyon at 2:00PM. • Informational Briefing Notice • Briefing Materials |
1/14/2026 | Hawaiʻi State Legislature | House Committee on Finance Badyet Briefing for the Kagawaran ng Edukasyon at 1:00PM. • Informational Briefing Notice • Briefing Materials |
1/9/2026 | Hawaiʻi State Legislature | House Committee on Edukasyon Briefing for the Kagawaran ng Edukasyon at 2:00PM. • Informational Briefing Notice |
1/7/2026 | Department of Taxation | The Council on Revenues held a meeting to forecast revenue growth for the General Fund on January 7th, 2026. • The Council kept the forecast for Fiscal Years (FY) 2026 through 2032 unchanged from the projections adopted at its last meeting on September 4, 2025. Accordingly, the General Fund growth forecast of the Council was as follows: -4.7% for FY 2026, 2.0% for FY 2027, 1.9% for FY 2028, 2.5% for FY 2029, 1.8% for FY 2030, 3.1% for FY 2031, and 3.4% for FY 2032. • Attachment 1 • Attachment 2 • Attachment 3 • Presentation |
1/1/2026 | Kagawaran ng Edukasyon | |
12/22/2025 | Governor | Gov. Green Submits the FY27 Supplement Badyet to the Legislature. Key Highlights of the FY27 Supplemental Badyet: • Mental Health: $8 million in general funds for Hawaii State Hospital. • Food Security: $13.4 million in general funds for SNAP. • Homelessness Solutions: $8 million in general funds. • Healthcare Infrastructure: $50 million in G.O. Bond funds. • Healthcare Access: $30 million in general funds and $30 million in federal funds for Medicaid technology upgrades. Forty-five million in general funds and $65 million in federal funds for the Medicaid program. • Emergency Healthcare Services: $8.1 million in general funds. • Climate Resiliency: First‑year implementation of the Governor’s Green Fee. |
11/26/2025 | Department of Budget and Finance | FM 25-24 Governor’s Decisions on FY 27 Supplemental Badyet Mga kahilingan FM 25-24 Attachment (Only EDN) |
11/20/2025 | Hawaiʻi State Legislature | |
11/13/2025 | Department of Budget and Finance | FM 25-22 Department of Budget and Finance’s Recommendations on FY 27 Supplemental Badyet Mga kahilingan • FM 25-22 Attachment (Only EDN) |
10/15/2025 | Department of Budget and Finance | EM 25-04 Amendments to Executive Memorandum No. 25-03, FY26 Badyet Execution Policies and Instructions • Revised Exhibit 1 |
10/15/2025 | Kagawaran ng Edukasyon | |
10/10/2025 | Kagawaran ng Edukasyon | |
10/9/2025 | Board of Education Finance and Infrastructure Committee meeting | Proposed Supplemental FY27 Badyet Request: • Operating Badyet – Agenda Item IV • CIP Badyet – Agenda Item V |
10/1/2025 | Department of Budget and Finance | FM 25-17 Supplement to Finance Memorandum No. 25-13, FY 27 Badyet Policies and Guidelines (Fiscal Biennium 2025-27) • This memorandum provides policies and guidelines for the preparation of supplemental budget requests relating to ACT 96, SLH 2025 “Green Fee.” |
9/12/2025 | Department of Budget and Finance | FM 25-13 FY 27 Supplemental Badyet Policies and Guidelines (Fiscal Biennium 2025-27) • Attachment 1 • Major, Recurring, List of Federal Awards State FY2027 |
9/4/2025 | Department of Taxation | The Council on Revenues held a meeting to forecast revenue growth for the General Fund on September 9th, 2025. • For Fiscal Year (FY) 2026, the Council lowered its forecast from -3.5% to -4.7%, but for FY 2027, it raised its forecast from 1.0% to 2.0%. The growth forecast for the FY 2028-2030 were changed as follows: From 1.5% to 1.9% for FY 2028, from 2.6% to 2.5% for FY 2029, and from 1.9% to 1.8% for FY 2030. The growth forecast for FY 2031 was unchanged at 3.1% and for FY 2032, it was set at 3.4%. • Presentation |
8/18/2025 | Department of Budget and Finance | |
6/30/2025 | Governor | HB300 Badyet Bill signed into law and enacted as ACT 250, SLH 2025 • DOE programs (EDN 100, 150, 200, 300, 400, and 500) start on page 32. • GIA’s start on page 58. • Capital Improvement Projects with EDN program codes start on page 134. |
5/27/2025 | Governor | SB1396 signed into law and enacted as ACT 96, SLH 2025, also known as Green Fee. • Purpose: Establishes the state’s first climate impact fee, increasing the Transient Accommodations Tax (TAT) by 0.75% to fund environmental stewardship and climate change mitigation efforts. |
5/21/2025 | Department of Taxation | The Council on Revenues held a meeting to forecast revenue growth for the General Fund on May 21st, 2025. • The Council lowered its forecast to 4.4% from 5.0% for Fiscal Year (FY) 2025. It also lowered the forecast to -3.50% from -2.25% for FY 2026, 1.0% from 2.9% for FY 2027, and 1.5% from 2.5% for FY 2028. The growth forecast for FYs 2029, 2030, and 2031 was left unchanged at 2.6%, 1.9%, and 3.1%, respectively. • Presentation |
5/2/2025 | Legislature | House Finance and Senate Ways and Means releases Committee Report and bill format of budget bill HB300 SD1. • Badyet Worksheet (see EDN 100, 150, 200, 300, 400, and 500) |
4/16/2025 | Department of Taxation | The Council on Revenues held a meeting to forecast revenue growth for the General Fund on March 12th, 2025. • The Council lowered its forecast to 5.0% from 6.4% for Fiscal Year (FY) 2025. It also lowered the forecast to -2.25% from -1.5% for FY 2026. The forecast for FYs 2027, 2028, 2029, 2030, and 2031 was left unchanged at 2.9%, 3.5%, 2.6%, 1.9%, and 3.1%, respectively. • Presentation |
4/8/2025 | Legislature | Senate Ways and Means releases Committee Report and bill format of budget bill HB300 SD1. • Badyet Worksheet (see EDN 100, 150, 200, 300, 400, and 500) |
3/11/2025 | Legislature | House Finance releases Committee Report and bill format of budget bill HB300 HD1. • Badyet Worksheet (see EDN 100, 150, 200, 300, 400, and 500) |
1/21/2025 | Legislature | Badyet Bill Introduced HB300 |
1/14/2025 | Legislature | Senate Committee on Ways and Means and Education budget briefing for the Kagawaran ng Edukasyon at 1:00 PM. • Informational Briefing Notice • Briefing Materials |
1/13/2025 | Legislature | House Committee on Education Budget Briefing for the Kagawaran ng Edukasyon at 2:00 PM. • Informational Briefing Notice |
1/10/2025 | Department of Taxation | The Council on Revenues held a meeting to forecast revenue growth for the General Fund on January 8th, 2025. • The Council increased the FY 2025 forecast and lowered the forecast for FY 2026-2029. • Presentation |
1/10/2025 | Legislature | House Committee on Finance Badyet Briefing for the Kagawaran ng Edukasyon at 9:00AM. • Informational Briefing Notice • Briefing Materials |
12/12/2024 | Board of EducationFinance and Infrastructure Committee meeting | Update on Governor’s Decision on FB 2025-27 Badyet: • CIP Badyet – Agenda Item III • Operating Badyet – Agenda Item IV |
11/27/2024 | Department of Budget and Finance | FM 24-17 Governor’s Decisions on FB 2025-27 Executive Badyet Requests: • FM 24-17 Attachment – EDN (Pg. 1-30) |
11/25/2024 | Hawaii State Legislature | |
11/13/2024 | Department of Budget and Finance | FM 24-16 Department of Budget and Finance’s Recommendations on FB 2025-27 Executive Badyet Requests: • FM 24-16 Attachment – EDN (Pg. 1-25) |
10/22/2024 | Board of EducationFinance and Infrastructure Committee meeting | |
9/26/2024 | Department of Budget and Finance | FM 24-10 Fiscal Biennium 2025-27 Executive Badyet Request and the Program and Financial Plan for the Period 2025-31: • Attachment 1 • Attachment 2 • Attachment 3 • Attachment 4 • Attachment 5 • Attachment 6 • Attachment 7 |
9/17/2024 | Department of Budget and Finance | |
9/10/2024 | Department of Taxation | The Council on Revenues held a meeting to forecast revenue growth for the General Fund on September 5th, 2024. • While the Council expects relatively solid economic growth for the current and subsequent fiscal years, it lowered its forecast because of the significant tax relief legislation passed in the 2024 Legislature. • Presentation |
7/26/2024 | Department of Budget and Finance | FM 24-07 Program Memoranda for Major Programs in the Statewide Program Structure |
7/9/2024 | Governor | HB1800 Badyet Bill signed into law and enacted as ACT 230, SLH 2024 • DOE programs (EDN 100, 150, 200, 300, 400, and 500) start on page 40. • GIA’s start on page 68. • Capital Improvement Projects with EDN program codes start on page 201 |
5/31/2024 | Department of Budget and Finance | FM 24-05 Review of the Program Structure and Performance Measures. • Edukasyon – FB 25-27 Executive Badyet Program Structure |
Operating Badyet
Mga Pinagmumulan ng Pagpopondo
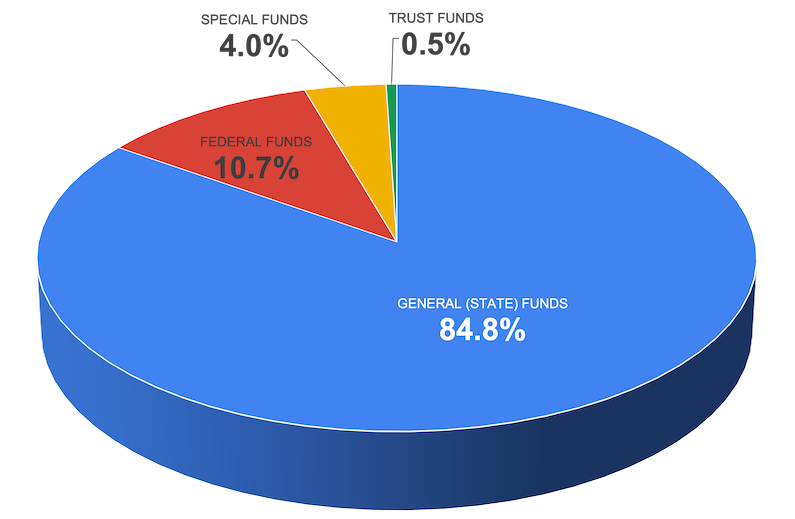
The fiscal year 2024-25 operating budget funding comes from four sources:
- Pangkalahatang pondo: Represents approximately 85% of our funding resources. Comes from the State of Hawaiʻi’s general fund, primarily state tax revenues. This is the top source of funding to the Department.
- Pederal na pondo: The second largest source of funding represents approximately 11% in expenditure ceiling resources. The Department receives grants from federal agencies including the U.S. Departments of Education, Agriculture, Defense and Health and Human Services.
- Mga espesyal na pondo: Roughly 4% of our expenditure ceiling resource is through special funds. Those coming from revenue-generating activities, including school food services, student bus transportation services, summer school program, after-school programs, adult education, driver education, and use of school facilities.
- Trust funds: Maaaring kasama ang mga donasyon at regalo, mga pundasyon at iba pang mga gawad, mga koleksyon ng aktibidad sa programang pampalakasan sa paaralan, at “patas na bahagi”.
Direct-to-School Funding
- EDN 100 ay halos ganap na ipinamamahagi sa mga paaralan gamit ang Weighted Student Formula (WSF). The WSF gives schools a specific dollar amount for each student, and additional funds for students with certain characteristics, such as qualifying for the free and reduced lunch program (socio-economically challenged) or being English language learners. This creates a transparent model of funding equity on a statewide basis. The balance of EDN 100 is used to support programs such as athletics, JROTC and Alternative Learning Centers.
- EDN 150 sumusuporta special education students who may require or have an Individualized Edukasyon Plan.
- EDN 400 nagbabayad ng mga bayarin sa paaralan kabilang ang imburnal, kuryente, tubig, pagkukumpuni, serbisyo sa pagkain at iba pa.
- EDN 500 pays for Adult Edukasyon programs at public schools.
Suportahan ang Pagpopondo sa Mga Antas ng Paaralan, Distrito, at Estado
The remainder of the budget is spread among EDNs 200 and 300, which provide support at all levels. These include instructional supports, statewide testing, administrative support (personnel, technology and fiscal), community programs such as A+ and adult education, complex area administration, the early learning opisina to provide pre-kindergarten programs, as well as the Board of Education at Office of the Superintendent.
Agencies (By EDN) that Operate Outside of the Kagawaran ng Edukasyon
- EDN 407 Mga Pampublikong Aklatan
- EDN 450 Awtoridad sa Pasilidad ng Paaralan
- EDN 600 Mga Paaralang Charter
- EDN 612 Komisyon at Pangangasiwa ng Charter Schools
- EDN 700 Executive Opisina on Early Learning
Non-facility general fund per-pupil funding request for charter school students
The general fund per-pupil amounts, not including charter school facilities (CIP) shall be the same as the general fund per-pupil for HIDOE schools as explained in HRS 302D-28.
- The process involves two phases, first, a budget appropriation request and then later, an allocation “true-up” to adjust for any differences.
- For the budget appropriation request, the Department of Budget and Finance Director of Finance submits to the Legislature a request based on projections for consideration in the final Badyet Appropriations Act [HRS 302D-28(a) and (b)].
- The appropriation request is reflected in the Charter School’s per pupil program.
- For the budget appropriation request, the Department of Budget and Finance Director of Finance submits to the Legislature a request based on projections for consideration in the final Badyet Appropriations Act [HRS 302D-28(a) and (b)].
- After the Appropriations Act is finalized, the Director of Finance ensures that an allocation “true up” is done using the October 15th student enrollment count. The true up equalizes the per-pupil funding for both entities [HRS 302D-28(c)]
Capital Improvements Program (CIP)
Ang Capital improvement Badyet (CIP) budget is set by the state as part of a comprehensive program to manage state facilities, and is handled separately from the operating budget. Facilities staff work with complex area superintendents and principals to prioritize school-level needs.
Badyet Allocations
Below are links to databases containing allocations for Department offices, districts, and schools. You can view the data by allocation number, program or organization.
